On February 26th I gave a talk at the Seattle Pecha Kecha #60, Watch Me Now, Notes on a Surveillance Society. The event brought together speakers from across the information ecosystem – including policy makers, technologists, advocates and others to discuss the complex issues surrounding privacy and surveillance in the digital world.
For this talk I discussed some of the themes that inspired the formation of Third Place Technologies — the power and perils of participating in public discourse online in the age of social media.
Here Be Dragons
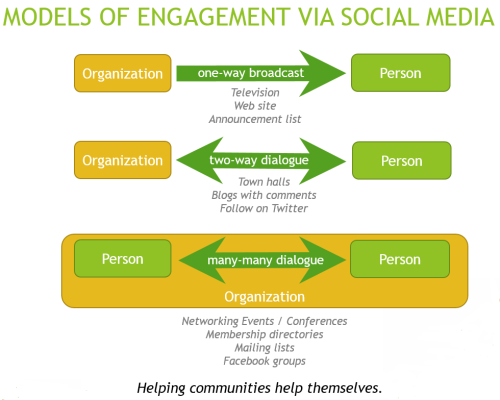
As noted by Bennett et al., (2009), the mere act of participation in public discourse online is a form of civic engagement as people share their personal stories, find people with similar interests and concerns, and then start working together to solve their collective problems. We have consistently found in our own research (e.g., Farnham et al. 2013) that it is the use of public networks (such as Twitter, blogs) that most corresponded with civic engagement, not, the use of personal networks (such as Facebook).
However, not all voices are equally represented in public spheres online. For example, while there are roughly an equal number of men and women with Twitter accounts, 64% of private account are women vs. 36% of men. (See statistics on beevolve.com.) In other words, women are not using social media to participate in public discourse as much as men are.
The story of #YesAllWomen provides a compelling example of the power and perils of online social media. This Twitter hashtag started in response to Elliott Rodger’s killing spree in May of 2014, where he killed 7 people including himself. To explain his murderous actions he posted a Youtube video stating “you girls have never been attracted to me, but I will punish you for it”. This chilling event evoked a strong reaction for many women, and within days, 1.2 million posted on Twitter their stories of fear of harassment and sexual assault from men who were similarly angry for not receiving sexual attention from them, under the hashtag #YesAllWomen. For many women, this outpouring of stories proved an empowering experience, giving a collective voice to everyday experiences that need to addressed. Unfortunately, the stream of messages was also interspersed with threatening and antifeminist posts. Within days, the woman who had created the original #YesAllWomen hashtag received so many threats she had to change her account to private.
In other words, she was silenced. This is not an unusual occurrence, many are silenced from participating in the public sphere through real or anticipated threats of intimidation. For example, Anita Sarkeesian, a feminist influential who was speaking out against the violence against women in video games, receives hundreds of abusive Tweets every week including death and rape threats. Just recently she received a mass shooting threat for a scheduled talk at Utah State, which she felt impelled to cancel because there was not sufficient security. (Learn more here.) She also was silenced, though she assures us only temporarily.
Outspoken feminists experiencing systematic intimidation are just one example of the perils of participating in the public sphere — there are many, many others; ranging from a gay teacher posting marriage announcements on Facebook and losing his job, to an anti drug cartel advocate in Reynosa, Mexico who was murdered for her Tweets reporting on their crimes.
Given the importance of being able to engage in the public sphere online, how can we help design third places technologies to assure the benefits of having a public voice online are experienced without harm by all?
As I mentioned in this talk, it is important to recognize that online environments can be hostile, much like work environments can be hostile, characterized by the cumulative effect of conduct in social media so severe and pervasive it interferes with a citizen’s ability to engage in public discourse. Systematic acts of intimidation through threats of violence are not free speech — they are the opposite of free speech, specifically designed to prevent a citizen from engaging in public discourse. As such, it is important to develop systems for civic discourse that adopt a zero tolerance policy toward such acts of intimidation.
Similarly, in cases where disclosing civic opinions might negatively impact a person’s well-being — such as job loss, public shaming, physical harm, or even loss of life — it’s extremely important to ensure participants have the right tools for privacy and identity segmentation. For example, I should be able to actively engage in authentic discourse around my political beliefs without my persona as an engaged citizen being tied to my persona as an employee or a family member. In face-to-face situations we can handle identity segmentation quite effectively simply by changing places (home, work, town hall), but have difficulty doing so in online systems that tend to collapse our social contexts — and identities — together.
Tools such as Twitter and Reddit are more appropriate for civic discourse than tools such as Facebook, because they enable pseudonymity. This is an identity separate from the “real” you, so that participation in public discourse online does not easily lead to personal harm offline. Yet, this online identity is persistent, and may develop its own reputation over time, which increases accountability and socially appropriate behavior. In this case, you might think of Twitter and Reddit as playing the role of identity brokers — a trusted, third party environment where individuals may disclose personal information.
That said, these systems have far to go before they are safe environments for people to express their public voice. Going forward, it is important to advocate social policy fostering a culture of respect online, recognizing that threats and bullying online can lead to real harm offline. Similarly there needs to be the appropriate legal adaptations balancing free speech and the principle of no harm. However as technologists, there is also much we can do in our socio-technical system designs to mitigate real threats to well-being. How we may design new technologies to ensure equitable participation and voice in the public sphere is a hard problem to solve, and an important theme of our work here at Third Place Technologies.
Here are the slides from the talk: Designing for the Perils of Public Voice in the Age of Social Media
References:
Bennett, W. L., Wells, C., and Freelorn, D. 2009. Communicating citizenship online: models of civic learning in the youth web sphere. Civic Learning Online Project.
Farnham, S.D., Keyes, D., Yuki, V., and Tugwell, C. (2013). Modeling youth civic engagement in the new world of networked publics. AAAI International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media (ICWSM).